Extinction: Are We Responsible?
EXTINCTION: ARE WE RESPONSIBLE? (ISSUE 167) FEBRUARY 24, 2015
By Diane Gold
 Let’s talk about Extinction and Loss Of Species, and are we responsible?
Let’s talk about Extinction and Loss Of Species, and are we responsible?
Yes, of course, we know that biology of a species, weather conditions, habitat destruction and ocean overuse, air quality or availability of whatever the species needs to breathe, food availability, water pollution, how the inhabitants of a planet nurture it and natural planetary cycle, all have to do with how long a species survives and how strong that species is.
Today’s article is written by our friend and colleague, Richard Oppenlander, D.D.S., dedicated researcher, who is one of the premier experts on how our food choices affect the sustainability of and species on our planet. He, in his very evidence-based and organized fashion, brings us information on how our food choices tie us to extinction and loss of species.
His last sentence is our ACTION STEP.
BIODIVERSITY AND FOOD CHOICE
by Richard Oppenlander (originally published at comfortablyunaware.com.)
 There needs to be a correction, and also modification of a particular concept, to the recently published article I had written for the North American Vegetarian Society (“Meat: no longer just a factory farm issue” in Vegetarian Voice 2012) regarding biodiversity loss.
There needs to be a correction, and also modification of a particular concept, to the recently published article I had written for the North American Vegetarian Society (“Meat: no longer just a factory farm issue” in Vegetarian Voice 2012) regarding biodiversity loss.
The “30,000 per year” extinction or loss of species statement I made is actually referring to species of animals, plants, insects—not simply animals (although the “animal” kingdom technically includes insects).
This figure was first brought to light by Harvard naturalist and emeritus professor of biology, Edward Wilson (The Diversity of Life, Harvard University Press 1992) and supported by Niles Eldridge (Life in the Balance, Princeton University Press 1998). Others such as Georgina Mace, Paul Ehrlich have extinction estimates as high as 70,000 to 130,000 species per year (7,000 to 13,000 times the background rate).
After speaking with and interviewing numerous researchers with the Species Survival Commission of IUCN (The World Conservation Union) and COBD (The Convention on Biological Diversity), about this topic over the past four months, I now feel there are many uncertainties surrounding attempts at quantifying the exact number of species becoming extinct per year. For this reason, it is more meaningful to view our planet’s current loss of species and the impact of our food choices in the following manner:
 1) We are losing species of life as well as ecosystems on Earth at an unprecedented and alarming rate, estimated to be anywhere between 1,000 and 10,000 times the “background rate”—that which had been seen for the previous several thousands of years. Therefore, it is this massive rate of extinction rather than number of loss that becomes a more meaningful metric and cause for concern.
1) We are losing species of life as well as ecosystems on Earth at an unprecedented and alarming rate, estimated to be anywhere between 1,000 and 10,000 times the “background rate”—that which had been seen for the previous several thousands of years. Therefore, it is this massive rate of extinction rather than number of loss that becomes a more meaningful metric and cause for concern.
 2) It is difficult, if not impossible, to accurately predict the number of species loss per year because of a number of factors. One of the largest unknowns is the exact amount of species that we have on earth, which is a needed component when attempting to determine total numbers of species loss when using an extinction prediction equation. This is one of the reasons the Species Area Curve Relationship method of extinction calculation has led to speculation and wide ranges of numbers of extinct species.
2) It is difficult, if not impossible, to accurately predict the number of species loss per year because of a number of factors. One of the largest unknowns is the exact amount of species that we have on earth, which is a needed component when attempting to determine total numbers of species loss when using an extinction prediction equation. This is one of the reasons the Species Area Curve Relationship method of extinction calculation has led to speculation and wide ranges of numbers of extinct species.
It is the feeling of most researchers today that although we have identified approximately 1.8 million species on our planet, there are most likely between 10 and 30 million that exist.
3) Regardless of the exact number of species becoming extinct per year, it is alarming at best and can be most attributed to loss of habitat—and the predicted future escalation will be due to habitat loss combined with climate change.
4) With estimates of 45% of all the land mass on Earth used by animal agriculture and 1 to 2 trillion fish extracted from our oceans each year (by fishing methods such as trawling, purse seine, long lines, explosives and other techniques that are damaging ecosystems)—eating animals (fishing and livestock production) is the largest contributing factor in habitat loss and constitutes the second largest sector implicated in anthropogenic [human caused] greenhouse gas emissions which lead to climate change.
 There has been widespread thought that marine species were more resilient to extinction and our further exploitation. However, there is finally a growing amount of evidence that fish and wildlife in our oceans are as, or more, vulnerable to extinction than many terrestrial and freshwater species. Extinction – Fish Vulnerable To Extinction
There has been widespread thought that marine species were more resilient to extinction and our further exploitation. However, there is finally a growing amount of evidence that fish and wildlife in our oceans are as, or more, vulnerable to extinction than many terrestrial and freshwater species. Extinction – Fish Vulnerable To Extinction
Despite continued massive harvesting of sea life from our oceans, it is generally agreed upon by researchers not affiliated with sustainable certifying organizations that the amount and distribution of threatened marine species is, at best, “poorly known.” Our demand to eat fish cannot be taken out of the equation when discussing our abuse of natural resources, eventual loss of species, and climate change.
Habitat loss is far and away the most pervasive threat to terrestrial animal species, impacting 86% of all mammals, 88% of amphibians, and 86% of all birds. One in every eight birds, one in every three amphibians and one in every four mammals is facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the near future. Overexploitation of animals for consumption remains a second major factor for extinction such as can be seen in wild meat trade in Africa and Southeast Asia and all hunting endeavors on land, globally.
Current biodiversity assessments (Millennium Ecosystem Assessment, IUCN Red List, and the Global Environmental and Biodiversity Outlook) now generally agree that land use change, modification of river flow, freshwater pollution, and exploitation of marine environments are the most significant drivers of biodiversity change and loss of species. Eventually, ocean acidification and climate change will become increasingly important. With overharvesting sea life in our oceans and raising livestock on land (grazing or CAFOs [factory farms]), our demand to eat animals and animal products remains the largest contributing anthropogenic factor to those accepted drivers of loss of species on Earth.

Let’s eat plants, not animals, and inspire others to do the same.
RICHARD OPPENLANDER
Dr. Richard Oppenlander is a researcher who studies the effects of food choices on health and environment. A dentist by day, he lectures about how animal agriculture is the biggest driver of global depletion and talks about solutions we can implement. He has written Comfortably Unaware and Food Choice And Sustainability, both flowing books with a wealth of scientific back up about how our food choices affect our land, oceans, water, air, soil, health. A copy of both books resides in my local public library ready to be read. And yours?
![]()
If you wish to share your story, please hit reply in your email program to be contacted.
If you need habit help, go to warriorsofweight-consulting.
![]()
FEEDBACK
We value your feedback very much.
Please leave a comment below.
Please LIKE us on the website and at
WarriorsOfWeight on Facebook.
You can also follow us on Twitter @warriorsoweight.
Thanks.
![]()
DIANE GOLD, PUBLISHER AND AUTHOR
Diane Gold, Founder of Warriors of Weight, Turning Habits Into Health, is a mentor in tai chi, kung fu and meditation, a music, fitness and stress expert, dedicated mom, studying plant-based nutrition in certificate course, peaceful conflict resolution and habit replacement.
She is so pleased to bring Richard Oppenlander. She says,
“Richard brings with him the honesty to speak about what we eat and how these choices affect our planet. He is always interested in the truth, and, at the same time, cares about the lives of animals. He offers the idea that becoming moderate will not work because we won’t be able to change our climate and our planet in time if we take our time. His message is clear, and that is to stop eating animals, fish, fowl, dairy and eggs.
“I second that, since I think it is the right way to live.
“And, finally, let us all take good care of ourselves, because we are so worth it!”
![]()

 Making a difference is certainly subjective. There’s no disputing, though, that every move we make changes something. While one person might plant spices to get personal produce, someone else might be a mentor in a literacy program and another someone else might create a way to keep food stored more efficiently. Yet another person might be the clerk in a grocery store or someone’s car washer.
Making a difference is certainly subjective. There’s no disputing, though, that every move we make changes something. While one person might plant spices to get personal produce, someone else might be a mentor in a literacy program and another someone else might create a way to keep food stored more efficiently. Yet another person might be the clerk in a grocery store or someone’s car washer. Food labeling is big, because, in order to notice what we eat, we have to know what’s in and on our food. And, our regulating agency, the Food & Drug Administration, has a slow and archaic way of labeling so that most of us don’t know what’s in and on our food. The chemical name for an ingredient doesn’t tell us if it is derived from animal, plant, microbe or a synthetic substance, and, wax coatings on produce don’t have a requirement to be as specific as I would like.
Food labeling is big, because, in order to notice what we eat, we have to know what’s in and on our food. And, our regulating agency, the Food & Drug Administration, has a slow and archaic way of labeling so that most of us don’t know what’s in and on our food. The chemical name for an ingredient doesn’t tell us if it is derived from animal, plant, microbe or a synthetic substance, and, wax coatings on produce don’t have a requirement to be as specific as I would like. One of the most important things to me is to make certain people realize that every time we make a choice, we effect something. This includes the space in which we live, the air we breathe, the water we need, our forests and jungles and the other creatures with whom we share the planet. When we farm animals, we are using their lives at our whim. Plus, if all we care about is human advantage, animal agriculture depletes more resources than anything else. So we are not protecting our own interests.
One of the most important things to me is to make certain people realize that every time we make a choice, we effect something. This includes the space in which we live, the air we breathe, the water we need, our forests and jungles and the other creatures with whom we share the planet. When we farm animals, we are using their lives at our whim. Plus, if all we care about is human advantage, animal agriculture depletes more resources than anything else. So we are not protecting our own interests.
 WarriorsofWeight.com Water Campaign For Thanksgiving is a mission to build a well for 500-1,000 people to give them access to a clean water supply for 10 years,
WarriorsofWeight.com Water Campaign For Thanksgiving is a mission to build a well for 500-1,000 people to give them access to a clean water supply for 10 years,  Can we look at it this way? Each of us, in whatever countries we are, has chosen to build water systems around borderlines, within the boundaries of our own country or union of countries. This is how we’ve always done it. We take care of our own. It doesn’t mean this is the way to continue to do it, should we choose to think of everyone as our own.
Can we look at it this way? Each of us, in whatever countries we are, has chosen to build water systems around borderlines, within the boundaries of our own country or union of countries. This is how we’ve always done it. We take care of our own. It doesn’t mean this is the way to continue to do it, should we choose to think of everyone as our own.
 Our habit of war is based upon our upbringing. We learn to stand up for ourselves, but we are not always groomed in the world of tolerance and forgiveness. We are taught that courage means fighting for our place, rather than showing that changing someone’s mind through talk is far braver.
Our habit of war is based upon our upbringing. We learn to stand up for ourselves, but we are not always groomed in the world of tolerance and forgiveness. We are taught that courage means fighting for our place, rather than showing that changing someone’s mind through talk is far braver. An example of successful use of pride can be seen in the first people in the United States, American Indians, whose connotation “Native Americans” currently includes Alaskan Natives, Native Hawaiians and American Samoans. In order for these groups to live in peace on land that was acquired by their ancestors, they had to participate willingly in a process of cooperation, compromise and huge sacrifice. They chose to be proud of their heritage at the same time as they agreed to give some land to get security, restitution and to live in peace. (When I say successful pride, I use the word “success” to mean making the best of a not so good situation.
An example of successful use of pride can be seen in the first people in the United States, American Indians, whose connotation “Native Americans” currently includes Alaskan Natives, Native Hawaiians and American Samoans. In order for these groups to live in peace on land that was acquired by their ancestors, they had to participate willingly in a process of cooperation, compromise and huge sacrifice. They chose to be proud of their heritage at the same time as they agreed to give some land to get security, restitution and to live in peace. (When I say successful pride, I use the word “success” to mean making the best of a not so good situation.

 There would be 3 sets of peace conferences: the first, with representatives at the Secretary of State level. If no agreement were reached here, the second conference would include military commanders at a high level. If no agreement were reached through conference with these individuals, the third conference would include the second in command of the respective territory/country.
There would be 3 sets of peace conferences: the first, with representatives at the Secretary of State level. If no agreement were reached here, the second conference would include military commanders at a high level. If no agreement were reached through conference with these individuals, the third conference would include the second in command of the respective territory/country. Prejudice is a habit we can replace. We are not born with it. It is part of our training: at home, in school, in the neighborhood, from peer pressure, peer example (social proof) and from the media.
Prejudice is a habit we can replace. We are not born with it. It is part of our training: at home, in school, in the neighborhood, from peer pressure, peer example (social proof) and from the media. The complex ways in which our minds are colored in a certain direction usually come from wanting comfort such as personal protection or to fit into a crowd or feel good about ourselves.
The complex ways in which our minds are colored in a certain direction usually come from wanting comfort such as personal protection or to fit into a crowd or feel good about ourselves. When someone takes our land, in the name of the individual, a cause, a race, a religion; we have a reaction. Because we have been taught that we have the rights to our land, we may equate this takeover with looting and attribute such looting to an entire group of a billion people, for whom we develop prejudice, even if only 50 people were involved.
When someone takes our land, in the name of the individual, a cause, a race, a religion; we have a reaction. Because we have been taught that we have the rights to our land, we may equate this takeover with looting and attribute such looting to an entire group of a billion people, for whom we develop prejudice, even if only 50 people were involved. The solution to replace any habit is to replace the behavior we do when we get the urge that we get. From my experience and from the time it takes our hormones to activate, I calculate we have 15 seconds. This takes into account how strongly and fervently our mind will grab onto our old habit and act accordingly. So, if we have previously done nothing when we have the urge to resolve the conflicts with the particular neighbors who wronged us, our reward, or the result of our actions, is a negative reward. We end up frustrated, angry, forlorn because we have been violated in some way by an entire group. The final reward of this non-action that we do is, you guessed it, prejudice. This is our justification for many irrational, out of scope future actions and current feelings we have.
The solution to replace any habit is to replace the behavior we do when we get the urge that we get. From my experience and from the time it takes our hormones to activate, I calculate we have 15 seconds. This takes into account how strongly and fervently our mind will grab onto our old habit and act accordingly. So, if we have previously done nothing when we have the urge to resolve the conflicts with the particular neighbors who wronged us, our reward, or the result of our actions, is a negative reward. We end up frustrated, angry, forlorn because we have been violated in some way by an entire group. The final reward of this non-action that we do is, you guessed it, prejudice. This is our justification for many irrational, out of scope future actions and current feelings we have.
 What if Nike’s logo meant food for the poor plus water, clothing, shelter, health care? Or Apple’s or ExxonMobil’s? What if these multinational corporations’
What if Nike’s logo meant food for the poor plus water, clothing, shelter, health care? Or Apple’s or ExxonMobil’s? What if these multinational corporations’
 Imagine Apple 2.0 Corporation, worth the $500 billion it is now, focusing its primary attention on helping people get adequate and healthy food, clothing and shelter. And all their artists, designers, technicians and computer scientists were putting full effort into creating the best ways to feed, hydrate, clothe, care for and house everyone adequately.
Imagine Apple 2.0 Corporation, worth the $500 billion it is now, focusing its primary attention on helping people get adequate and healthy food, clothing and shelter. And all their artists, designers, technicians and computer scientists were putting full effort into creating the best ways to feed, hydrate, clothe, care for and house everyone adequately. What does it mean to be civilized? Does it mean being more sophisticated by wearing upscale and fancy clothing while we pillage the environment to get raw materials to manufacture modern comforts OR does it mean living sustainably without taking more than is necessary for community survival while insuring the rebirth of the resources used for survival?
What does it mean to be civilized? Does it mean being more sophisticated by wearing upscale and fancy clothing while we pillage the environment to get raw materials to manufacture modern comforts OR does it mean living sustainably without taking more than is necessary for community survival while insuring the rebirth of the resources used for survival?
 The answer is not as mind boggling as I thought it was. It’s right in front of you and me. It’s tithing, an old English unit meaning one-tenth of something. Much of the developing country manipulation could be monitored, and every corporation that made over one billion one hundred eleven million dollars would be required to give 10% of its gross profit to those in need for food, clothing, shelter, water and health care. The collector of this profit would have to be an independent agent, a non-government, non-profit establishment that published all incoming and outgoing funding to the public.
The answer is not as mind boggling as I thought it was. It’s right in front of you and me. It’s tithing, an old English unit meaning one-tenth of something. Much of the developing country manipulation could be monitored, and every corporation that made over one billion one hundred eleven million dollars would be required to give 10% of its gross profit to those in need for food, clothing, shelter, water and health care. The collector of this profit would have to be an independent agent, a non-government, non-profit establishment that published all incoming and outgoing funding to the public.
 Profit From Peace is an ideal that has fallen through the cracks in discussions at the university level, in primary and secondary schools, across diplomatic and corporate tables. It’s not really in the back of our minds, yet, either.
Profit From Peace is an ideal that has fallen through the cracks in discussions at the university level, in primary and secondary schools, across diplomatic and corporate tables. It’s not really in the back of our minds, yet, either. Each candidate would pitch the business plan of her/his created company, including how to finance and manage it. The show would include role playing a board meeting run by the prospective director of the company.
Each candidate would pitch the business plan of her/his created company, including how to finance and manage it. The show would include role playing a board meeting run by the prospective director of the company. We already know how to make money from war. Military equipment, location and protection technology and gear, air, land and sea vehicles need manufacturing, technological assembly, fuel for transport, human personnel, financing up front to pay for the above, medical costs during and after war. We have mastered this art. Let’s explore another.
We already know how to make money from war. Military equipment, location and protection technology and gear, air, land and sea vehicles need manufacturing, technological assembly, fuel for transport, human personnel, financing up front to pay for the above, medical costs during and after war. We have mastered this art. Let’s explore another. BUSINESS INVESTORS
BUSINESS INVESTORS 1)
1)  Hopefully, the profit from peace concept is now embedded in our minds. It can only grow as we talk and refine it. If we are consistent, don’t disrespect the profit position of war manufacturers and give them an alternative; we might have embarked upon something that will work.
Hopefully, the profit from peace concept is now embedded in our minds. It can only grow as we talk and refine it. If we are consistent, don’t disrespect the profit position of war manufacturers and give them an alternative; we might have embarked upon something that will work.
 What makes the above quote a great definition is that Charles Darwin alludes to something similar in his Origin of the Species as did his predecessor, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, 500 years before Darwin. They both arrived at the idea that traits can be passed down generationally even if they are acquired through acquired training of the previous generations. Another way of saying this would be that the offspring of parents who are trained in a certain behavior are born with the behavior and no previous training in the future generations.
What makes the above quote a great definition is that Charles Darwin alludes to something similar in his Origin of the Species as did his predecessor, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, 500 years before Darwin. They both arrived at the idea that traits can be passed down generationally even if they are acquired through acquired training of the previous generations. Another way of saying this would be that the offspring of parents who are trained in a certain behavior are born with the behavior and no previous training in the future generations.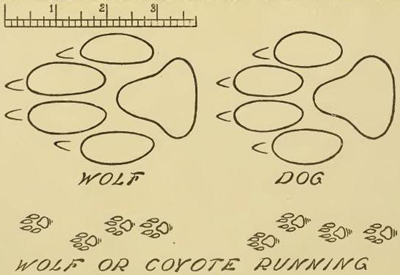 We can look at the domestication of one or two wolf species. The domesticated wolf became the dog, according to James Serpell, professor at University of Pennsylvania’s School of Vet Medicine in his 1995 The Domestic Dog. Through teaching the wolf pup of the wild wolf to be calm, gentle and social with humans; the offspring of the tamed wolf pups began to exhibit the gentler traits at birth, without any training.
We can look at the domestication of one or two wolf species. The domesticated wolf became the dog, according to James Serpell, professor at University of Pennsylvania’s School of Vet Medicine in his 1995 The Domestic Dog. Through teaching the wolf pup of the wild wolf to be calm, gentle and social with humans; the offspring of the tamed wolf pups began to exhibit the gentler traits at birth, without any training. So, the way of our evolution has to do with the training we are given which, if ingrained in us well, can be passed down to our offspring or to their future generations from birth. What could exist is our own domestication, cultivating the habit of peaceful coexistence.
So, the way of our evolution has to do with the training we are given which, if ingrained in us well, can be passed down to our offspring or to their future generations from birth. What could exist is our own domestication, cultivating the habit of peaceful coexistence. The point here is if we start role playing peaceful solutions to different circumstances when we are young, we will be very experienced at conflict resolution by the time we reach 25 when our voices can help run the world. We will recognize human rights violations and know how to use our voices against them using our peaceful methods. This means we may be interested in letting go of our old ways.
The point here is if we start role playing peaceful solutions to different circumstances when we are young, we will be very experienced at conflict resolution by the time we reach 25 when our voices can help run the world. We will recognize human rights violations and know how to use our voices against them using our peaceful methods. This means we may be interested in letting go of our old ways.